Your Which of the following processes are types of post translational protein modification images are available. Which of the following processes are types of post translational protein modification are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Which of the following processes are types of post translational protein modification files here. Get all royalty-free images.
If you’re searching for which of the following processes are types of post translational protein modification images information linked to the which of the following processes are types of post translational protein modification interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Which Of The Following Processes Are Types Of Post Translational Protein Modification. Carboxylation of glutamate for increased calcium sequestration 6. Protein splicing is a post-translational modification process in which an internal protein segment an intein excises itself from a surrounding external protein which it ligates to form the mature extein. Physiological functions of glycoprotein glycans are important topics in postgenomic era. This is often added to a serine tyrosine or threonine amino acid residue.
 Post Translational Modification From slideshare.net
Post Translational Modification From slideshare.net
Phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Just so how many post translational modifications are there. Types Of Post Translational Modifications. Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. More than 200 diverse types of PTMs are currently known 56 ranging from small chemical modifications eg phosphorylation and acetylation to the addition of complete proteins eg ubiquitylation Figure 3. Post-translational modifications take place in the ER and include folding glycosylation multimeric protein assembly and proteolytic cleavage leading to protein maturation and activation.
More than 200 diverse types of PTMs are currently known 56 ranging from small chemical modifications eg phosphorylation and acetylation to the addition of complete proteins eg ubiquitylation Figure 3.
What are the two most common methods of post translation modification of proteins. A kinase is the. Types of post-translational modification. Carboxylation of glutamate for increased calcium sequestration 6. They take place as soon as the growing peptide emerges in the ER and is exposed to modifying enzymes. Some proteins typically targeted to membranes will be lipidated - a lipid will be added.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
They take place as soon as the growing peptide emerges in the ER and is exposed to modifying enzymes. More than 200 diverse types of PTMs are currently known 56 ranging from small chemical modifications eg phosphorylation and acetylation to the addition of complete proteins eg ubiquitylation Figure 3. Some proteins typically targeted to membranes will be lipidated - a lipid will be added. Another common post-translational modification is cleavage or linking of parts of the protein itself. In the human body these PTMs increases the diversity and accuracy of proteins.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Types Of Post Translational Modifications. Phosphorylation Which of the following steps occurs last in the initiation phase of translation. Protein post-translational modifications PTMs increase the functional diversity of the proteome by the covalent addition of functional groups or proteins proteolytic cleavage of regulatory subunits or degradation of entire proteins. Some proteins typically targeted to membranes will be lipidated - a lipid will be added.
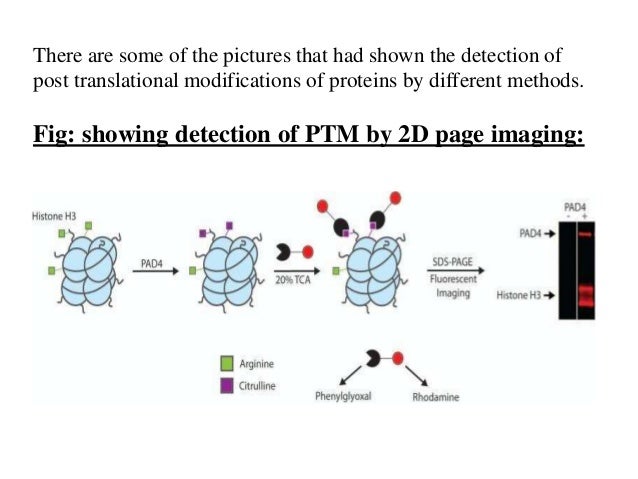 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Ubiquitination to designate proteins for degradation by the proteosome. The post translational modifiactions can be enzymatic or covalent. Protein post-translational modifications PTMs increase the functional diversity of the proteome by the covalent addition of functional groups or proteins proteolytic cleavage of regulatory subunits or degradation of entire proteins. Types of post-translational modification. Types of post-translational modification.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
They take place as soon as the growing peptide emerges in the ER and is exposed to modifying enzymes. Types of post-translational modification. Protein glycosylation is the most prominent among various types of post-translational protein modifications. What are the two most common methods of post translation modification of proteins. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein causing it to become activated deactivated or modifying its function.
 Source: proteinwalls.blogspot.com
Source: proteinwalls.blogspot.com
Carboxylation of glutamate for increased calcium sequestration 6. Acetylation and methylation of histone proteins 5. In the human body these PTMs increases the diversity and accuracy of proteins. Physiological functions of glycoprotein glycans are important topics in postgenomic era. The following are the common types of Post-translational Modifications.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Phosphorylation Which of the following steps occurs last in the initiation phase of translation. Sulfation is a permanent post- translational modification needed for the functioning of the proteins. This is often added to a serine tyrosine or threonine amino acid residue. Protein glycosylation is the most prominent among various types of post-translational protein modifications. Protein splicing is a post-translational modification process in which an internal protein segment an intein excises itself from a surrounding external protein which it ligates to form the mature extein.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Protein glycosylation is the most prominent among various types of post-translational protein modifications. B Post-translational modifications play important roles in diverse cell functions as intracellular signaling phosphorylation regulation of protein stability ubiquitination regulation of transcription histone acetylation and methylation and cell surface signaling glycosylation. Phosphorylation is a type of post-translational modification that adds a phosphate group to a protein. Ubiquitination to designate proteins for degradation by the proteosome. 100 28 ratings Post translational modification events include Phosporylation Glycosylation and Ubiquitination Phosphorylation The most important post translational modification is Phosporylation of serine threo view the full answer.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Protein splicing is a post-translational modification process in which an internal protein segment an intein excises itself from a surrounding external protein which it ligates to form the mature extein. Common modifications include phosphate groups methyl acetate and amide groups. Sulfation is a permanent post- translational modification needed for the functioning of the proteins. The post translational modifiactions can be enzymatic or covalent. Which processes are types of post translational protein modification.
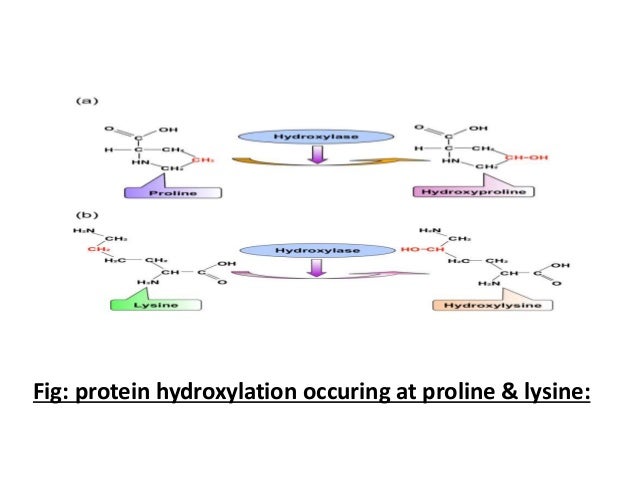 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Which of the following processes is an example of a post-translational modification. Physiological functions of glycoprotein glycans are important topics in postgenomic era. Which of the following processes is an example of a post-translational modification. Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Post translational modifications or PTMs are involved in modifying the protein structure after they have been translated according to information on the mRNA.
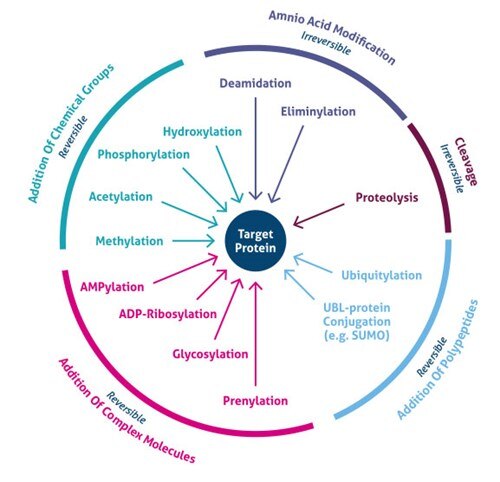 Source: ptglab.com
Source: ptglab.com
Types of post-translational modification. Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein causing it to become activated deactivated or modifying its function. Acetylation and methylation of histone proteins 5. Ubiquitination to designate proteins for degradation by the proteosome.
Source: journals.plos.org
Sulfation is a permanent post- translational modification needed for the functioning of the proteins. Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Types of post-translational modification. The post translational modifiactions can be enzymatic or covalent. Ubiquitination to designate proteins for degradation by the proteosome.
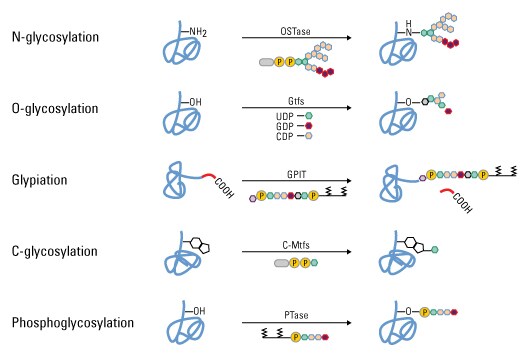 Source: thermofisher.com
Source: thermofisher.com
More than 200 diverse types of PTMs are currently known 56 ranging from small chemical modifications eg phosphorylation and acetylation to the addition of complete proteins eg ubiquitylation Figure 3. What are the two most common methods of post translation modification of proteins. Protein glycosylation is the most prominent among various types of post-translational protein modifications. Acetylation and methylation of histone proteins 5. Types of post-translational modification.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Physiological functions of glycoprotein glycans are important topics in postgenomic era. The following are the common types of Post-translational Modifications. Phosphorylation Which of the following steps occurs last in the initiation phase of translation. Just so how many post translational modifications are there. More than 200 diverse types of PTMs are currently known 56 ranging from small chemical modifications eg phosphorylation and acetylation to the addition of complete proteins eg ubiquitylation Figure 3.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Another common post-translational modification is cleavage or linking of parts of the protein itself. Ubiquitination to designate proteins for degradation by the proteosome. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. 100 28 ratings Post translational modification events include Phosporylation Glycosylation and Ubiquitination Phosphorylation The most important post translational modification is Phosporylation of serine threo view the full answer. They take place as soon as the growing peptide emerges in the ER and is exposed to modifying enzymes.
 Source: news-medical.net
Source: news-medical.net
100 28 ratings Post translational modification events include Phosporylation Glycosylation and Ubiquitination Phosphorylation The most important post translational modification is Phosporylation of serine threo view the full answer. B Post-translational modifications play important roles in diverse cell functions as intracellular signaling phosphorylation regulation of protein stability ubiquitination regulation of transcription histone acetylation and methylation and cell surface signaling glycosylation. They take place as soon as the growing peptide emerges in the ER and is exposed to modifying enzymes. The post translational modifiactions can be enzymatic or covalent. 100 28 ratings Post translational modification events include Phosporylation Glycosylation and Ubiquitination Phosphorylation The most important post translational modification is Phosporylation of serine threo view the full answer.
 Source: rockland-inc.com
Source: rockland-inc.com
Which processes are types of post translational protein modification. More than 200 diverse types of PTMs are currently known 56 ranging from small chemical modifications eg phosphorylation and acetylation to the addition of complete proteins eg ubiquitylation Figure 3. Which processes are types of post translational protein modification. Phosphorylation Which of the following steps occurs last in the initiation phase of translation. Protein glycosylation is the most prominent among various types of post-translational protein modifications.
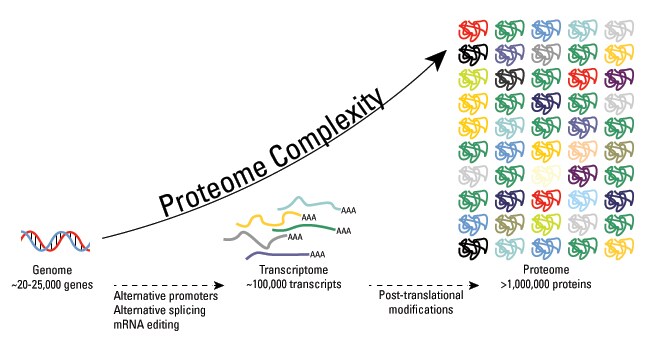 Source: thermofisher.com
Source: thermofisher.com
Phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Acetylation and methylation of histone proteins 5. Ubiquitination is another major post-translational modification that has a major role in protein degradation. Common modifications include phosphate groups methyl acetate and amide groups. Phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They take place as soon as the growing peptide emerges in the ER and is exposed to modifying enzymes. A kinase is the. Post translational modifications or PTMs are involved in modifying the protein structure after they have been translated according to information on the mRNA. Phosphorylation addition of phosphates 4. Types of post-translational modification.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title which of the following processes are types of post translational protein modification by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






