Your Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification images are ready. Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification files here. Get all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification images information linked to the which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification interest, you have visit the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Enzyme Regulation Through Covalent Modification. Covalent Enzyme modification. Enzyme Regulation For example mammalian cells both catabolize and synthesize glucose. Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity. Relate this to the enzyme activity.
 Regulation Of Enzyme Activity Ppt Video Online Download From slideplayer.com
Regulation Of Enzyme Activity Ppt Video Online Download From slideplayer.com
Here a donor molecule provides a functional moiety and this modifies the properties of the enzyme. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Under low energy conditions AMP will bind to phosphofructokinase 1 and glycogen phophorylase at a site unique to the active site. They are- Reversible covalent modification. In metabolic control modulation of enzyme activity by attaching or releasing tiny groups plays a very significant role. Cleavage Of Chymotrypsinogen To Chymotrypsin D. Covalent modification is a method of regulation of the activity of enzymes.
Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Movement of ammonia from an amino acid to an alpha-keto acid involves a family of enzymes best categorized as.
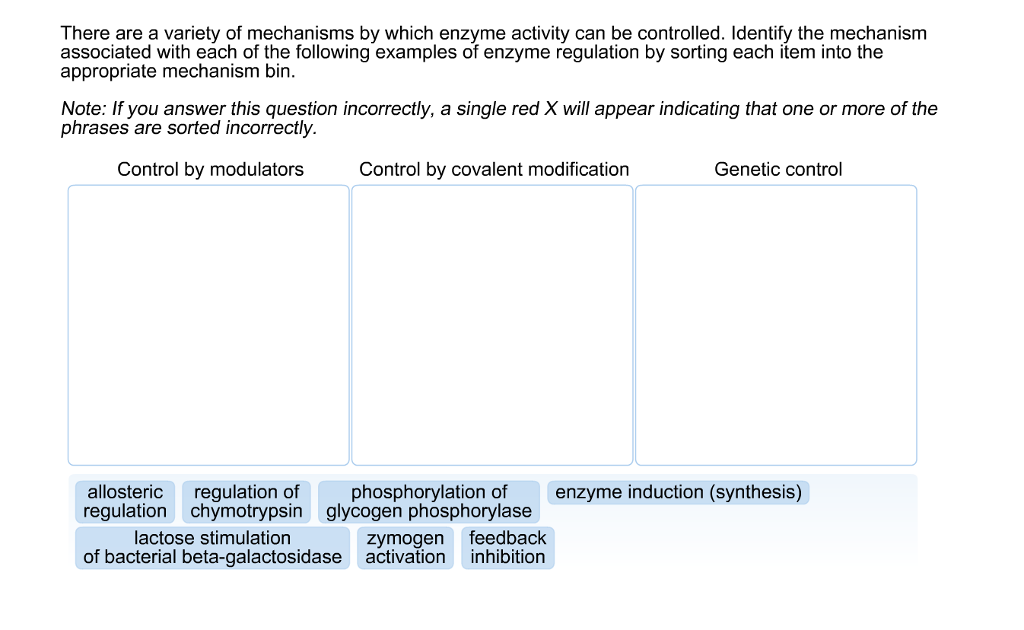
Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. See page 142 section B1. Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification. 2 out of 2 points Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification. CAMP cyclic adenosine monophosphate activates the enzyme. Question 2 Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Although its primary regulation is through covalent modification it is also modulated in a noncovalent allosteric manner by AMP which is an activator of phosphorylase b and several other molecules that are inhibitors. See page 142 section B1. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. Phosphorylation Of Muscle Glycogen Phosphorylase C. Phosphorylation of enzyme occurs by addition of phosphate group to the enzyme at the hydroxyl group of serine threonine or tyrosine.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Here a donor molecule provides a functional moiety and this modifies the properties of the enzyme. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Movement of ammonia from an amino acid to an alpha-keto acid involves a family of enzymes best categorized as. This enzyme is formed of 4 subunits 2 regulatory 2R and 2 catalytic 2C subunits. Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Response Feedback. See page 142. Allosteric regulation and feedback loops. Protein kinase A enzyme is an example for regulation of enzyme activity through protein interaction. Phosphorylation of enzyme occurs by addition of phosphate group to the enzyme at the hydroxyl group of serine threonine or tyrosine.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
See page 142 section B1. See page 142 section B1. Enzyme Regulation For example mammalian cells both catabolize and synthesize glucose. Cleavage Of Chymotrypsinogen To Chymotrypsin D. Although its primary regulation is through covalent modification it is also modulated in a noncovalent allosteric manner by AMP which is an activator of phosphorylase b and several other molecules that are inhibitors.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Question 2 Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Movement of ammonia from an amino acid to an alpha-keto acid involves a family of enzymes best categorized as. Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity. Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. See page 142.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Compare T vs R states within enzyme. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Under low energy conditions AMP will bind to phosphofructokinase 1 and glycogen phophorylase at a site unique to the active site. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Response Feedback. In metabolic control modulation of enzyme activity by attaching or releasing tiny groups plays a very significant role.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
See page 142. Otherwise energy is wasted by what is called a futile cycle carrying out opposing reactions at high rates with no net substrate flow in either direction. Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. This occurs by protein kinase enzyme. Protein kinase A enzyme is an example for regulation of enzyme activity through protein interaction.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Otherwise energy is wasted by what is called a futile cycle carrying out opposing reactions at high rates with no net substrate flow in either direction. Effect on enzyme activity. The covalent enzyme modification is mainly in two types. Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification. The whole enzyme 2R2C is inactive.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Protein kinase A enzyme is an example for regulation of enzyme activity through protein interaction. Figure 98 Phosphorylation is an example of covlent mofication. Modifications of enzymes is relevant and thats in reference to zymogens now as I imagine is an inactive form of an enzyme that requires a covalent modification or to become active and a big example of these zymogens in biology are the digestive enzymes that the pancreas releases so that you can. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Response Feedback. Enzyme Regulation For example mammalian cells both catabolize and synthesize glucose.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The rates at which these reactions occur must be regulated. Enzyme Regulation For example mammalian cells both catabolize and synthesize glucose. Here a donor molecule provides a functional moiety and this modifies the properties of the enzyme. Glycogen phosphorylase is an example. In certain enzymes the addition of a phosphate group to a specific amino acid residue usually serine Ser tyrosine Tyr or threonine Thr by specific protein kinases dramatically enhances or depresses activity.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Here a donor molecule provides a functional moiety and this modifies the properties of the enzyme. See page 142 section B1. Relate this to the enzyme activity. Allosteric regulation and feedback loops. Compare T vs R states within enzyme.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
In metabolic control modulation of enzyme activity by attaching or releasing tiny groups plays a very significant role. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Movement of ammonia from an amino acid to an alpha-keto acid involves a family of enzymes best categorized as. Cleavage Of Chymotrypsinogen To Chymotrypsin D. Effect on enzyme activity. Cleavage of chymotrypsinogen to chymotrypsin Correct Answer.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity. Phosphorylation of enzyme occurs by addition of phosphate group to the enzyme at the hydroxyl group of serine threonine or tyrosine. Figure 98 Phosphorylation is an example of covlent mofication. Phosphorylation Of Muscle Glycogen Phosphorylase C. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Movement of ammonia from an amino acid to an alpha-keto acid involves a family of enzymes best categorized as.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Modifications of enzymes is relevant and thats in reference to zymogens now as I imagine is an inactive form of an enzyme that requires a covalent modification or to become active and a big example of these zymogens in biology are the digestive enzymes that the pancreas releases so that you can. Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. The rates at which these reactions occur must be regulated. Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Enzyme Regulation Through Covalent Modification.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Under low energy conditions AMP will bind to phosphofructokinase 1 and glycogen phophorylase at a site unique to the active site. See page 142 section B1. Covalent Enzyme modification. In certain enzymes the addition of a phosphate group to a specific amino acid residue usually serine Ser tyrosine Tyr or threonine Thr by specific protein kinases dramatically enhances or depresses activity. Cleavage Of Chymotrypsinogen To Chymotrypsin D.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
See page 142. In certain enzymes the addition of a phosphate group to a specific amino acid residue usually serine Ser tyrosine Tyr or threonine Thr by specific protein kinases dramatically enhances or depresses activity. Phosphorylation of the enzyme occurs by addition of phosphate group to the enzyme at the hydroxyl group of serine threonine or tyrosine. Figure 98 Phosphorylation is an example of covlent mofication. This enzyme is formed of 4 subunits 2 regulatory 2R and 2 catalytic 2C subunits.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Digestion Of Misfolded Proteins By Lysosomes B. This enzyme is formed of 4 subunits 2 regulatory 2R and 2 catalytic 2C subunits. Relate this to the enzyme activity. Question 2 Which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification. In certain enzymes the addition of a phosphate group to a specific amino acid residue usually serine Ser tyrosine Tyr or threonine Thr by specific protein kinases dramatically enhances or depresses activity.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Allosteric regulation and feedback loops. Cleavage Of Chymotrypsinogen To Chymotrypsin D. Protein kinase A enzyme is an example for regulation of enzyme activity through protein interaction. Phosphorylation of muscle glycogen phosphorylase Response Feedback. Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title which of the following is an example of enzyme regulation through covalent modification by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





