Your Which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity images are ready. Which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity images information linked to the which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity interest, you have come to the right site. Our website always provides you with hints for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Which Of The Following Is A Covalent Modification That Can Affect Enzyme Activity. This modification includes the addition or removal of chemical groups. They are- Reversible covalent modification. Methane acts as an electron donor. Phosphorylation is a covalent modification that controls the activity of enzymes and other proteins.
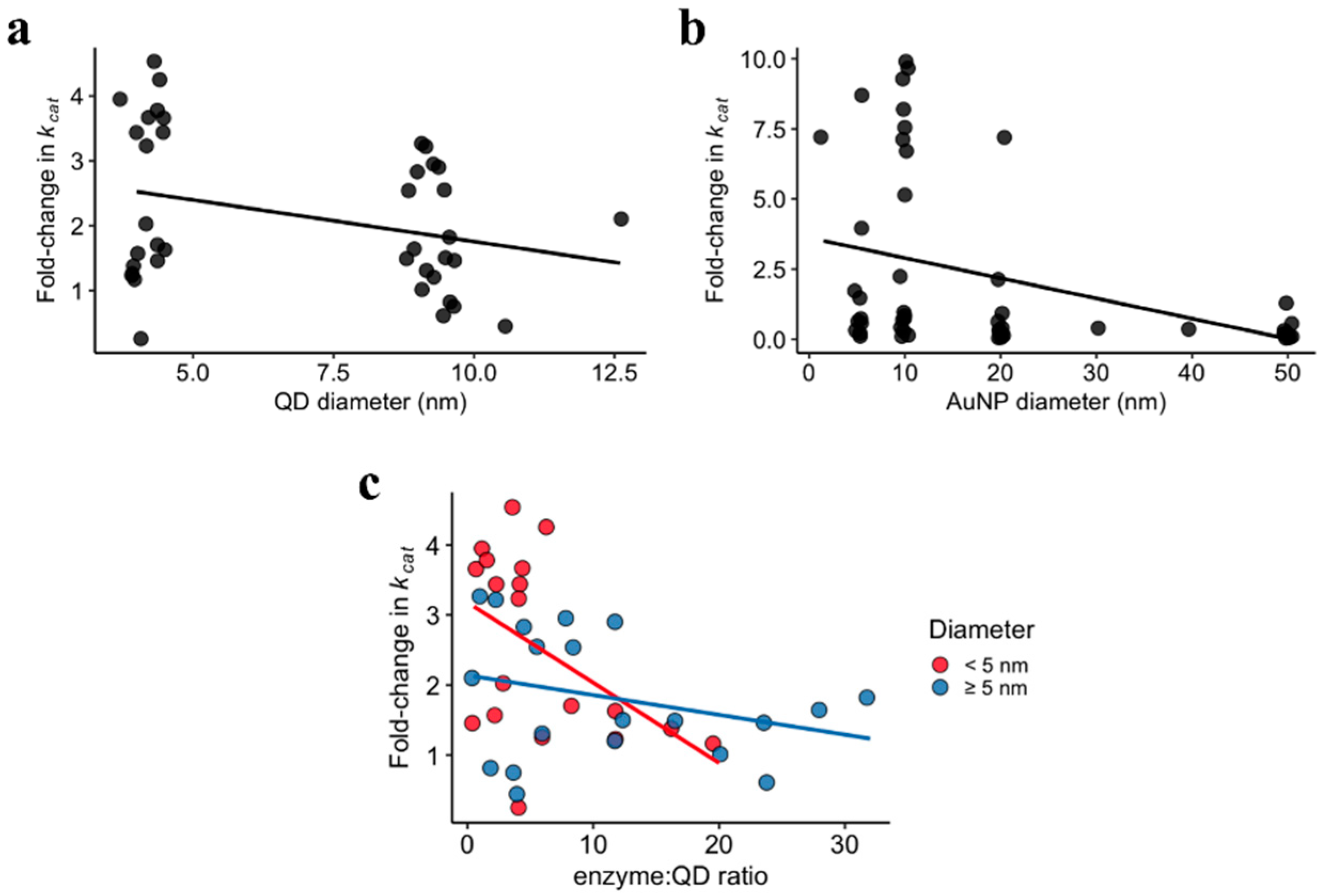 Catalysts Free Full Text Quantum Dots And Gold Nanoparticles As Scaffolds For Enzymatic Enhancement Recent Advances And The Influence Of Nanoparticle Size Html From mdpi.com
Catalysts Free Full Text Quantum Dots And Gold Nanoparticles As Scaffolds For Enzymatic Enhancement Recent Advances And The Influence Of Nanoparticle Size Html From mdpi.com
Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. Effect on enzyme activity. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of the protein within the cell. Therefor mass analysis of the. Covalent Modification vs Allosteric control Covalent Modification. Signals can be greatly amplified by this modification because one kinase has the potential to create an exponential chain effect on various target molecules.
This modification includes the addition or removal of chemical groups.
In certain enzymes the addition of a phosphate group to a specific amino acid residue usually serine Ser tyrosine Tyr or threonine Thr by specific protein kinases dramatically enhances or depresses activity. Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Modifications other than proteolysis leaving a soluble enzyme. 1 Allosteric is non covalent. They are- Reversible covalent modification. In covalent modification there is a change in the activity of enzyme upon addition of chemical group phosphorylation ie.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. 1 Allosteric is non covalent. Which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity. Effect on enzyme activity. In covalent modification there is a change in the activity of enzyme upon addition of chemical group phosphorylation ie.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. A required by all enzymes in the cell b loosely bound to enzymes via hydrogen bonds c sites on the enzyme molecule that permit allosteric modification of enzyme activity d linked to phosphate groups e tightly bound to enzymes and are required for their activity 3 The initial rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction depends on. Phosphorylation is a covalent modification that controls the activity of enzymes and other proteins. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of the protein within the cell. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage.
 Source: www2.nau.edu
Source: www2.nau.edu
Covalent Modification vs Allosteric control Covalent Modification. Modifications other than proteolysis leaving a soluble enzyme. A the concentration of the enzyme b the concentration of the substrate c the affinity of the enzyme. Phosphorylation The lowering of activation energy during the transition step of enzyme catalysis depends on ___________ at the enzymes active site. This modification includes the addition or removal of chemical groups.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. A required by all enzymes in the cell b loosely bound to enzymes via hydrogen bonds c sites on the enzyme molecule that permit allosteric modification of enzyme activity d linked to phosphate groups e tightly bound to enzymes and are required for their activity 3 The initial rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction depends on. They break large molecules into smaller parts and produce energy. A the concentration of the enzyme b the concentration of the substrate c the affinity of the enzyme. Considering the reaction CH4 methane plus O2 yields CO2 plus H2O plus energy which of the following is true.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Phosphorylation of the enzyme occurs by addition of phosphate group to the enzyme at the hydroxyl group of serine threonine or tyrosine. Methane acts as an electron donor. Which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity. They are- Reversible covalent modification. Covalent modifications all give rise to specific changes in MW.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The enzyme-catalyzed alterations of synthesized proteins are called covalent modification of enzymes. Covalent Modification vs Allosteric control Covalent Modification. Methane acts as an electron donor. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of. Phosphorylation of the enzyme occurs by addition of phosphate group to the enzyme at the hydroxyl group of serine threonine or tyrosine.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Phosphorylation The lowering of activation energy during the transition step of enzyme catalysis depends on ___________ at the enzymes active site. Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Methane acts as an electron donor. Effect on enzyme activity. Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity.
 Source: botnam.com
Source: botnam.com
Signals can be greatly amplified by this modification because one kinase has the potential to create an exponential chain effect on various target molecules. In case of other types of covalent modifications assuming the modified protein is still soluble the modified protein will probably still behave similarly to the intact protein in chromatographic procedures and can be purified accordingly. Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. In addition enzymes can be regulated via covalent modification or post-translational modification. Modifications other than proteolysis leaving a soluble enzyme.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Therefor mass analysis of the. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of the protein within the cell. Covalent modifications all give rise to specific changes in MW. This modification includes the addition or removal of chemical groups. Phosphorylation of the enzyme occurs by addition of phosphate group to the enzyme at the hydroxyl group of serine threonine or tyrosine.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Addition o view the full answer Previous question Next question. Modifications other than proteolysis leaving a soluble enzyme. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of. Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity. The covalent enzyme modification is mainly in two types.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Phosphorylation The lowering of activation energy during the transition step of enzyme catalysis depends on ___________ at the enzymes active site. Signals can be greatly amplified by this modification because one kinase has the potential to create an exponential chain effect on various target molecules. In addition enzymes can be regulated via covalent modification or post-translational modification. Methane acts as an electron donor. In covalent modification there is a change in the activity of enzyme upon addition of chemical group phosphorylation ie.
 Source: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
Source: openoregon.pressbooks.pub
In covalent modification there is a change in the activity of enzyme upon addition of chemical group phosphorylation ie. Which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity. They break large molecules into smaller parts and produce energy. A required by all enzymes in the cell b loosely bound to enzymes via hydrogen bonds c sites on the enzyme molecule that permit allosteric modification of enzyme activity d linked to phosphate groups e tightly bound to enzymes and are required for their activity 3 The initial rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction depends on. Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity.
 Source: pl.pinterest.com
Source: pl.pinterest.com
They break large molecules into smaller parts and produce energy. Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. That means that after the enzyme has been assembled in the cell its structure can be modified further by adding special groups to specific locations. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of. A the concentration of the enzyme b the concentration of the substrate c the affinity of the enzyme.
 Source: jbc.org
Source: jbc.org
Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity. 2 covalent modification requires enzymes to attach and remove the group whereas in allostery no additional enzymes are involved 3 covalent modification is a slower regulatory mechanism than allostery is. They are- Reversible covalent modification. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of. The enzyme-catalyzed alterations of synthesized proteins are called covalent modification of enzymes.
 Source: wou.edu
Source: wou.edu
Signals can be greatly amplified by this modification because one kinase has the potential to create an exponential chain effect on various target molecules. Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Many if not most proteins are subjected to post-translational modifications which can affect enzyme activity through local or global shape changes by promoting or inhibiting binding interaction of substrates and allosteric regulators and even by changing the location of. A required by all enzymes in the cell b loosely bound to enzymes via hydrogen bonds c sites on the enzyme molecule that permit allosteric modification of enzyme activity d linked to phosphate groups e tightly bound to enzymes and are required for their activity 3 The initial rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction depends on. Covalent Modification vs Allosteric control Covalent Modification.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
That means that after the enzyme has been assembled in the cell its structure can be modified further by adding special groups to specific locations. Addition o view the full answer Previous question Next question. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. Phosphorylation is the most covalent modification used to regulate enzyme activity. Signals can be greatly amplified by this modification because one kinase has the potential to create an exponential chain effect on various target molecules.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Modifications other than proteolysis leaving a soluble enzyme. In addition enzymes can be regulated via covalent modification or post-translational modification. That means that after the enzyme has been assembled in the cell its structure can be modified further by adding special groups to specific locations. They are- Reversible covalent modification. Phosphorylation is a covalent modification that controls the activity of enzymes and other proteins.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
They are- Reversible covalent modification. They break large molecules into smaller parts and produce energy. The enzyme-catalyzed alterations of synthesized proteins are called covalent modification of enzymes. In certain enzymes the addition of a phosphate group to a specific amino acid residue usually serine Ser tyrosine Tyr or threonine Thr by specific protein kinases dramatically enhances or depresses activity. Therefor mass analysis of the.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title which of the following is a covalent modification that can affect enzyme activity by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





