Your Which is not a posttranscriptional modification to the mrna images are available in this site. Which is not a posttranscriptional modification to the mrna are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Which is not a posttranscriptional modification to the mrna files here. Get all free photos.
If you’re looking for which is not a posttranscriptional modification to the mrna pictures information related to the which is not a posttranscriptional modification to the mrna keyword, you have come to the right blog. Our site always gives you hints for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
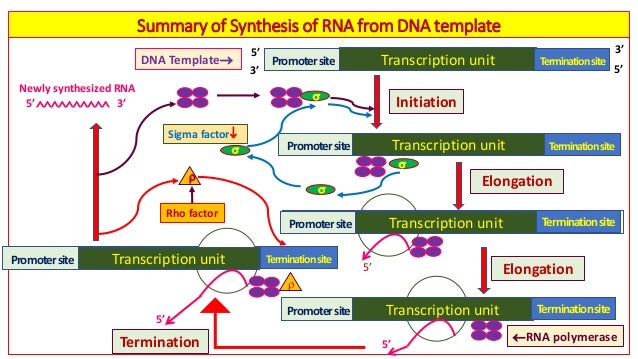
Which Is Not A Posttranscriptional Modification To The Mrna. Insertion of introns D. Post-transcriptional modification is a process in cell biology by which in eukaryotic cells primary transcript RNA is converted into mature RNA. When a eukaryotic gene is transcribed in the nucleus the primary transcript freshly made RNA molecule isnt yet considered a messenger RNA. This processing that takes place after an RNA molecule has been transcribed but before it is translated into a protein is called post-transcriptional modification.
 What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Mrna Pediaa Com Plant Protein Plant Protein Sources Biology Facts From pinterest.com
What Is The Difference Between Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Mrna Pediaa Com Plant Protein Plant Protein Sources Biology Facts From pinterest.com
E they are RNA-ases. To the 3 end of the RNA chain 30-500 adenines are added in what is called a poly A tail. The most frequently encountered mechanism consists in a post-transcriptional modification of the 23S rRNA by methylases usually named Erm erythromycin resistance methylase which add one or two methyl groups to a single adenine residue A2058 in. This processing that takes place after an RNA molecule has been transcribed but before it is translated into a protein is called post-transcriptional modification. The 3 terminus of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is usually modified by the addition of a polyadenosine sequence the poly-A tail of as many as 50 to 250 nucleotides. Primary transcript hnRNA must be processed to produce the mRNA active form.
Prokaryotic mRNA is generally identical to its primary transcript whereas eukaryotic mRNA is extensively modified co- and posttranscriptionally.
The identification and functional characterization of proteins that specifically recognize RNA N 6 -methyladenosine m 6 A unveiled it as a modification that cells utilize to accelerate mRNA metabolism and translation. Prokaryotic mRNA is generally identical to its primary transcript whereas eukaryotic mRNA is extensively modified co- and posttranscriptionally. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation. Example is one type of β-thalassemia. Modification of the ribosomal target causing reduction of affinity for their binding site can cause resistance to MLS antibiotics. The pre-mRNA has to go through some modifications to become a mature mRNA molecule that can leave the nucleus and be translated.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The coding sequences exons are interrupted by noncoding introns which must be removed to make a translatable mRNA. Post-transcriptional modifications of mRNA occur in the nucleus. MRNA transcribed directly from DNA template and used immediately in protein synthesis Eukaryotes. The 3 terminus of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is usually modified by the addition of a polyadenosine sequence the poly-A tail of as many as 50 to 250 nucleotides. Posttranslational modifications in peptide chains can also lead to increased protein stability and increased duration of action.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
To the 3 end of the RNA chain 30-500 adenines are added in what is called a poly A tail. And 3 modifications that code dynamic regulatory information on top of the primary sequence such as modifications on mRNA. The coding sequences exons are interrupted by noncoding introns which must be removed to make a translatable mRNA. If the RNA is not processed shuttled or translated then no protein will be synthesized. Post transcriptional modification Prokaryotes.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
What is Posttranscriptional Modification. Primary transcript hnRNA must be processed to produce the mRNA active form. A notable example is the conversion of precursor messenger RNA into mature messenger RNA mRNA which includes splicing and occurs prior to protein synthesis. Use a shorter poly-A-tail. 5-capping removal of exons.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
1 modifications that enforce certain RNA structures and tune RNA biogenesis such as modifications on rRNA and small nuclear RNA snRNA Dickmanns and Ficner 2005. To the 3 end of the RNA chain 30-500 adenines are added in what is called a poly A tail. What is Posttranscriptional Modification. The recent discovery of reversible mRNA methylation has opened a new realm of post-transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. MRNA exists for hoursdaysweeks not usable right away and it needs to be modified.
 Source: id.pinterest.com
Source: id.pinterest.com
The coding sequences exons are interrupted by noncoding introns which must be removed to make a translatable mRNA. The 3 terminus of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is usually modified by the addition of a polyadenosine sequence the poly-A tail of as many as 50 to 250 nucleotides. For the AP it is enough to know that mRNA is modified before leaving the cytoplasm and engaging in protein synthesis and that these modifications. The eukaryotic pre-mRNA undergoes extensive processing before it is ready to be translated. Primary transcript hnRNA must be processed to produce the mRNA active form.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Mutation that results in a nucleotide change at an exon-intron junction. The coding sequences exons are interrupted by noncoding introns which must be removed to make a translatable mRNA. It is thought to help with mRNA recognition by the ribosome during translation. A modification also takes place at the opposite end of the RNA transcript. Eukaryotic protein-coding sequences are not continuous as they are in prokaryotes.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
5-capping removal of exons. Faulty splicing may result in diseases. Post-transcriptional modifications of mRNA occur in the nucleus. The recent discovery of reversible mRNA methylation has opened a new realm of post-transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Mechanism that regulates erythromycin-induced resistance.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation. MRNA is degraded in minutes mRNA is usable right away and it does not need to be modified. Mechanism that regulateserythromycin-induced resistance. Insertion of introns D. It occurs in nucleas of cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Posttranslational modifications in peptide chains can also lead to increased protein stability and increased duration of action. The mature RNA then enters the cytosol to perform its function translation. The recent discovery of reversible mRNA methylation has opened a new realm of post-transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. And 3 modifications that code dynamic regulatory information on top of the primary sequence such as modifications on mRNA. Horinouchi S Weisblum B.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Modification of the mRNA molecule can be mediated by proteins or in some instances can be mediated by RNA sequences that have intrinsic enzymic activity i. A modification also takes place at the opposite end of the RNA transcript. RNA is transcribed but must be processed into a mature form before translation can begin. Mechanism that regulates erythromycin-induced resistance. Mechanism that regulateserythromycin-induced resistance.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The pre-mRNA has to go through some modifications to become a mature mRNA molecule that can leave the nucleus and be translated. To the 3 end of the RNA chain 30-500 adenines are added in what is called a poly A tail. Horinouchi S Weisblum B. 3-capping insertion of introns. Use a shorter poly-A-tail.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
3-capping insertion of introns. For the most part post-transcriptional processing is not covered in courses such as AP Biology. To the 3 end of the RNA chain 30-500 adenines are added in what is called a poly A tail. Most eukaryotic mRNAs also contain intervening sequences introns that must be removed to make the mRNA functional. For the AP it is enough to know that mRNA is modified before leaving the cytoplasm and engaging in protein synthesis and that these modifications.
 Source: fr.pinterest.com
Source: fr.pinterest.com
5-capping removal of exons. Post-transcriptional modifications of mRNA occur in the nucleus. For the most part post-transcriptional processing is not covered in courses such as AP Biology. Instead its an immature molecule called a pre-mRNA. It occurs in nucleas of cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Most eukaryotic mRNAs also contain intervening sequences introns that must be removed to make the mRNA functional. Insertion of introns D. Mechanism that regulateserythromycin-induced resistance. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation. For the AP it is enough to know that mRNA is modified before leaving the cytoplasm and engaging in protein synthesis and that these modifications.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Insertion of introns D. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation. Insertion of introns D. The pre-mRNA has to go through some modifications to become a mature mRNA molecule that can leave the nucleus and be translated. MRNA transcribed directly from DNA template and used immediately in protein synthesis Eukaryotes.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation. The 3 terminus of a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is usually modified by the addition of a polyadenosine sequence the poly-A tail of as many as 50 to 250 nucleotides. 1 modifications that enforce certain RNA structures and tune RNA biogenesis such as modifications on rRNA and small nuclear RNA snRNA Dickmanns and Ficner 2005. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation. Mutation that results in a nucleotide change at an exon-intron junction.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Mechanism that regulateserythromycin-induced resistance. Posttranscriptional modification of mRNA conformation. Prokaryotic mRNA is generally identical to its primary transcript whereas eukaryotic mRNA is extensively modified co- and posttranscriptionally. Modification of the ribosomal target causing reduction of affinity for their binding site can cause resistance to MLS antibiotics. 5-capping removal of exons.
 Source: za.pinterest.com
Source: za.pinterest.com
When a eukaryotic gene is transcribed in the nucleus the primary transcript freshly made RNA molecule isnt yet considered a messenger RNA. Example is one type of β-thalassemia. When a eukaryotic gene is transcribed in the nucleus the primary transcript freshly made RNA molecule isnt yet considered a messenger RNA. To the 3 end of the RNA chain 30-500 adenines are added in what is called a poly A tail. MRNA exists for hoursdaysweeks not usable right away and it needs to be modified.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title which is not a posttranscriptional modification to the mrna by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.