Your What are the major mechanisms of epigenetic genome modification images are available. What are the major mechanisms of epigenetic genome modification are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the What are the major mechanisms of epigenetic genome modification files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for what are the major mechanisms of epigenetic genome modification images information related to the what are the major mechanisms of epigenetic genome modification keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
What Are The Major Mechanisms Of Epigenetic Genome Modification. Epigenetic modifications can define how the information in genes is. There are three major processes of epigenetic modification. These mechanisms perpetuate individual gene expression programs to establish an epigenetic code that characterizes a cell. Epigenetics are heritable changes in gene expression that occur with no alteration in DNA sequence.
 Three Fundamental Mechanisms Of Epigenetic Gene Regulation Epigenetic Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Three Fundamental Mechanisms Of Epigenetic Gene Regulation Epigenetic Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Epigenetic modifications are stable heritable traits or phenotypes other than those which are based on genomic sequences. Select The Five Correct Answers. DNA methylation histone modification and non-coding RNAs including siRNA and miRNA. At least three systems including DNA methylation histone modifications and non-coding RNAs ncRNA are considered to. A number of epigenetic processes have been identified to play a role in IPF including the three major epigenetic mechanisms. Chromatin-modifying Enzymes Methylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Methyl And Phosphate Groups Binding Of RISC To Target MRNA Molecules DNA Acetylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Amino And Methoxy Groups DNA.
While much attention has been focused on the classical epigenetic mark 5-methylcytosine the field garnered increased interest through the recent discovery of additional modifications.
It is well known that these non-genetic alterations are strictly attributable to 3 major epigenetic modifications. That is if you include as methylation the opposite demethylation and acetylation deacetylation. During meiosis most epigenetic modifications to the genome are erased. Epigenetics the study of the chemical modification of specific genes or gene-associated proteins of an organism. Chromatin-modifying Enzymes Methylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Methyl And Phosphate Groups Binding Of RISC To Target MRNA Molecules DNA Acetylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Amino And Methoxy Groups DNA. Through epigenetics modifications to chromosomes take place and alter gene-expression patterns.
 Source: ysjournal.com
Source: ysjournal.com
Select The Five Correct Answers. To silence a gene it is coated with methyl or more rarely acetyl. However there is a second mechanism through which hereditary information is expressed. Epigenetic changes play an important role in malignant transformation and can be specific to types of cancers including prostate cancer. While much attention has been focused on the classical epigenetic mark 5-methylcytosine the field garnered increased interest through the recent discovery of additional modifications.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Epigenetic modifications can define how the information in genes is. Epigenetics the study of the chemical modification of specific genes or gene-associated proteins of an organism. The major epigenetic modifications include DNA methylation histone modification and non-coding RNA. It is well known that these non-genetic alterations are strictly attributable to 3 major epigenetic modifications. Epigenetics are heritable changes in gene expression that occur with no alteration in DNA sequence.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Epigenetics are heritable changes in gene expression that occur with no alteration in DNA sequence. Modification at the DNA level These modifications are cancelled during the process of. Direct DNA methylation chromatin histone modifications and noncoding RNAs ncRNAs. Histone modification can make some regions of the genome more open or closed for transcription. The chemical modification of DNA bases plays a key role in epigenetic gene regulation.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
There has been extensive research on the role of epigenetic mechanisms including aberrant DNA methylation histone modification and microRNA in the pathogenesis of T1D. The major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation. These mechanisms perpetuate individual gene expression programs to establish an epigenetic code that characterizes a cell. These are functionally relevant changes and modifications of genome that excludes modifications of nucleotide sequences. Epigenetic modifications can define how the information in genes is.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
There has been extensive research on the role of epigenetic mechanisms including aberrant DNA methylation histone modification and microRNA in the pathogenesis of T1D. Epigenetic modifications can define how the information in genes is. Modification at the DNA level These modifications are cancelled during the process of. These mechanisms perpetuate individual gene expression programs to establish an epigenetic code that characterizes a cell. All cells in the body contain DNA which is inherited from both of our parents at conception.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A number of epigenetic processes have been identified to play a role in IPF including the three major epigenetic mechanisms. Histone modification can make some regions of the genome more open or closed for transcription. One of the most remarkable properties of epigenetics modifications is that it is transmitted through cell generations. All cells in the body contain DNA which is inherited from both of our parents at conception. The major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation modification of histone proteins chemical modification and chromatin remodeling changes in gene expression caused by microRNAs miRNAs.
 Source: scienceofhealthy.com
Source: scienceofhealthy.com
Chromatin-modifying Enzymes Methylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Methyl And Phosphate Groups Binding Of RISC To Target MRNA Molecules DNA Acetylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Amino And Methoxy Groups DNA. The primary mechanisms of epigenetics are methylation histone modification and tagging. DNA methylation histone modifications and noncoding RNA see FIGURE 1. There has been extensive research on the role of epigenetic mechanisms including aberrant DNA methylation histone modification and microRNA in the pathogenesis of T1D. Epigenetic modifications can define how the information in genes is.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Epigenetics are heritable changes in gene expression that occur with no alteration in DNA sequence. While much attention has been focused on the classical epigenetic mark 5-methylcytosine the field garnered increased interest through the recent discovery of additional modifications. This mechanism is epigenetics 14 defined on the previous page. All these epigenetic mechanisms have important roles in the development of germ cells from primordial germ cell PGC differentiation and migration through meiotic process and maturation of functional gametes. The primary mechanisms of epigenetics are methylation histone modification and tagging.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Direct DNA methylation chromatin histone modifications and noncoding RNAs ncRNAs. DNA methylation histone modification and non-coding RNAs including siRNA and miRNA. For example the mechanisms of histone. Epigenetics acts mainly through four different mechanisms. This mechanism is epigenetics 14 defined on the previous page.
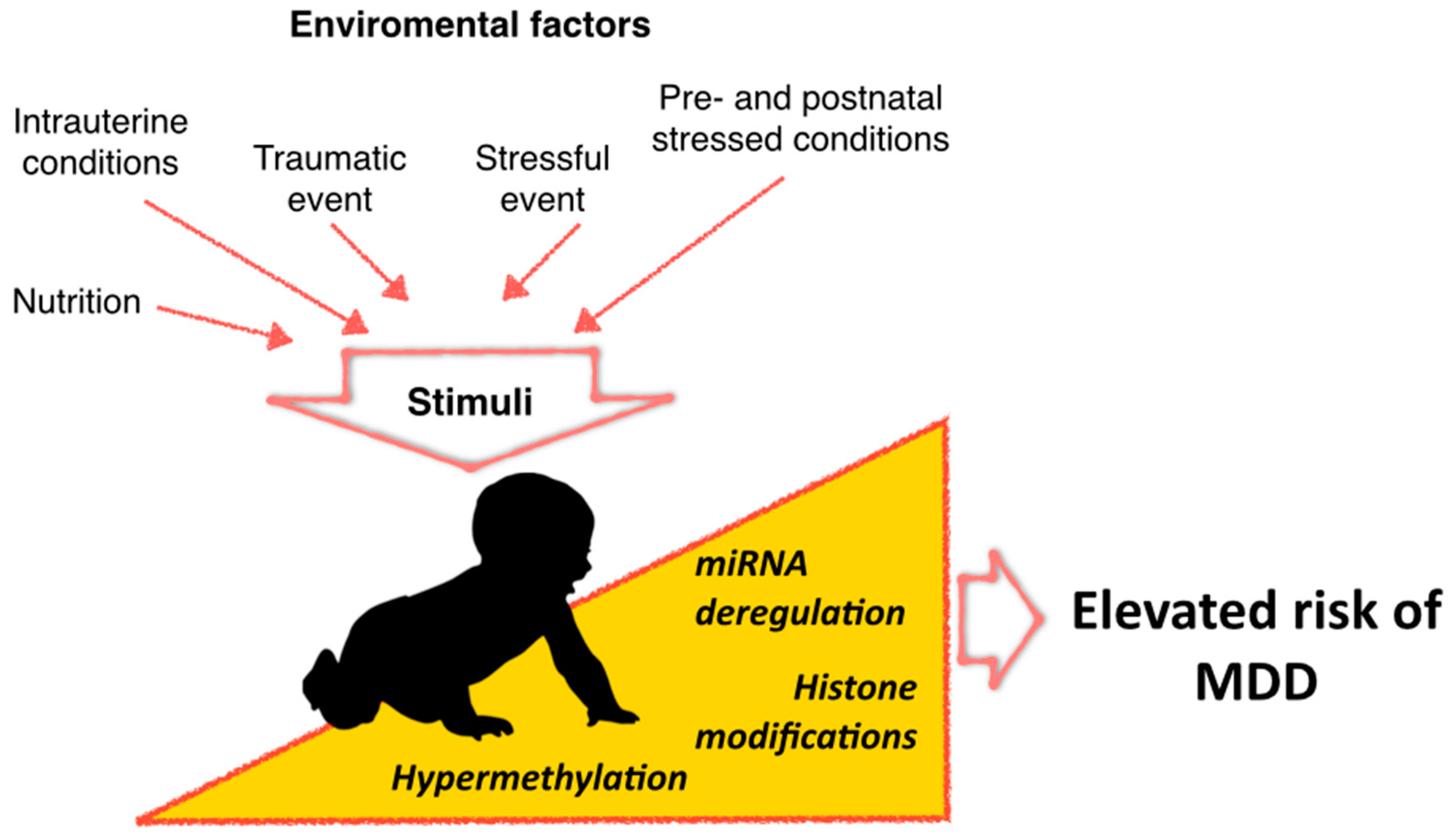 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
At least three systems including DNA methylation histone modifications and non-coding RNAs ncRNA are considered to. These mechanisms perpetuate individual gene expression programs to establish an epigenetic code that characterizes a cell. These are functionally relevant changes and modifications of genome that excludes modifications of nucleotide sequences. Histone modification can make some regions of the genome more open or closed for transcription. There are dynamic event that modulate the gene expression.
 Source: ysjournal.com
Source: ysjournal.com
However there is a second mechanism through which hereditary information is expressed. Through epigenetics modifications to chromosomes take place and alter gene-expression patterns. Epigenetic modifications comprise three main mechanisms DNA methylation chromatin structure modifications and noncoding RNA ncRNA. Histone modification can make some regions of the genome more open or closed for transcription. The major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation modification of histone proteins chemical modification and chromatin remodeling changes in gene expression caused by microRNAs miRNAs.
 Source: ysjournal.com
Source: ysjournal.com
Direct DNA methylation chromatin histone modifications and noncoding RNAs ncRNAs. During meiosis most epigenetic modifications to the genome are erased. There are three major processes of epigenetic modification. These mechanisms perpetuate individual gene expression programs to establish an epigenetic code that characterizes a cell. The major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation.
 Source: biologicalpsychiatryjournal.com
Source: biologicalpsychiatryjournal.com
Direct DNA methylation chromatin histone modifications and noncoding RNAs ncRNAs. One of the most remarkable properties of epigenetics modifications is that it is transmitted through cell generations. Epigenetic modifications comprise three main mechanisms DNA methylation chromatin structure modifications and noncoding RNA ncRNA. During meiosis most epigenetic modifications to the genome are erased. There has been extensive research on the role of epigenetic mechanisms including aberrant DNA methylation histone modification and microRNA in the pathogenesis of T1D.
 Source: novusbio.com
Source: novusbio.com
The major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation. Epigenetics investigates the mechanisms that affect gene expression without changing the DNA sequence. Chromatin-modifying Enzymes Methylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Methyl And Phosphate Groups Binding Of RISC To Target MRNA Molecules DNA Acetylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Amino And Methoxy Groups DNA. Epigenetics refers to mechanisms of gene expression regulation that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence. Epigenetics acts mainly through four different mechanisms.
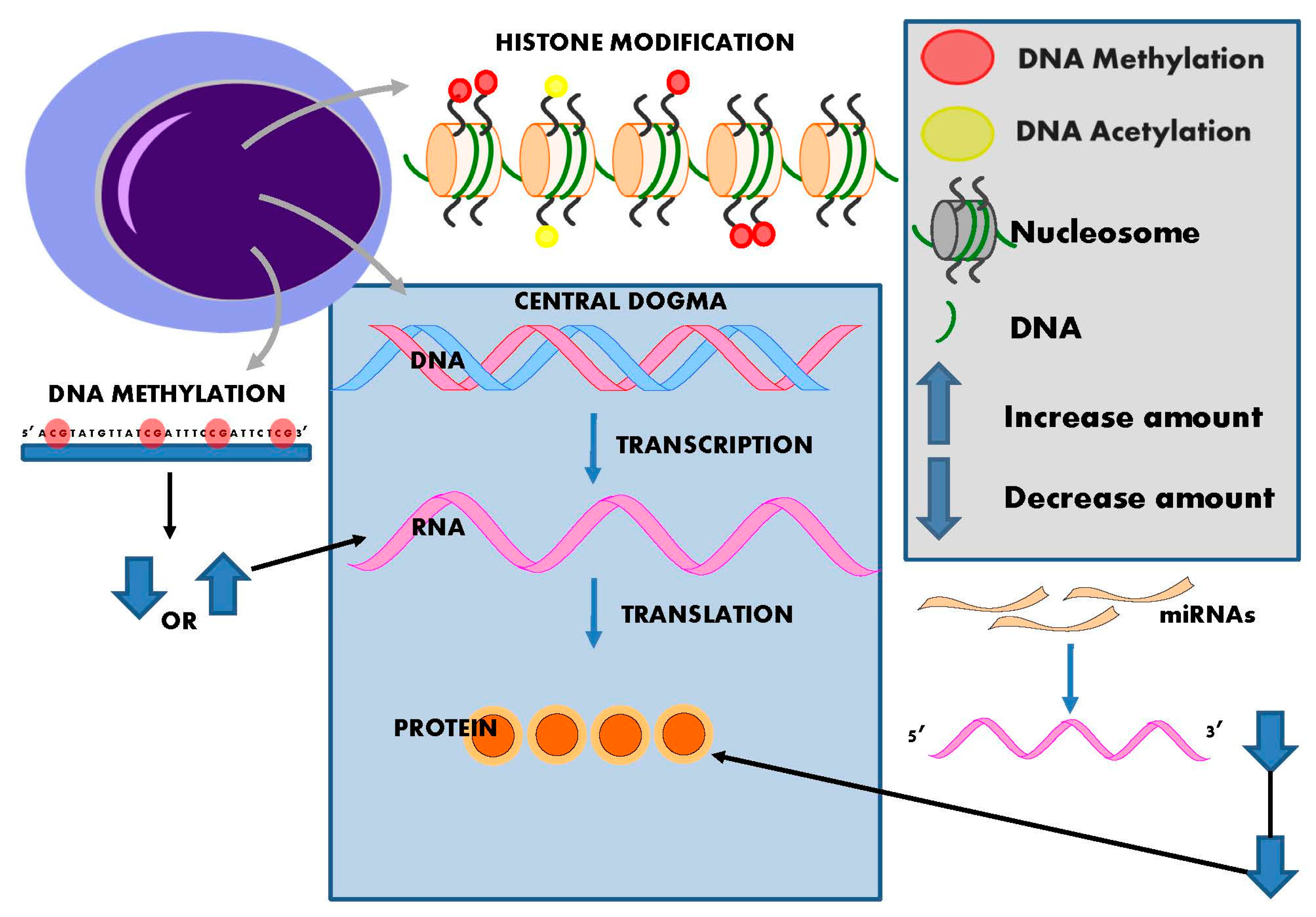 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Chromatin-modifying Enzymes Methylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Methyl And Phosphate Groups Binding Of RISC To Target MRNA Molecules DNA Acetylation Histone Modification Involving Acetyl Amino And Methoxy Groups DNA. A number of epigenetic processes have been identified to play a role in IPF including the three major epigenetic mechanisms. There are three major processes of epigenetic modification. All these epigenetic mechanisms have important roles in the development of germ cells from primordial germ cell PGC differentiation and migration through meiotic process and maturation of functional gametes. It is well known that these non-genetic alterations are strictly attributable to 3 major epigenetic modifications.
 Source: scienceofhealthy.com
Source: scienceofhealthy.com
There are dynamic event that modulate the gene expression. Epigenetic modifications are stable heritable traits or phenotypes other than those which are based on genomic sequences. Epigenetics acts mainly through four different mechanisms. The major epigenetic mechanisms include DNA methylation modification of histone proteins chemical modification and chromatin remodeling changes in gene expression caused by microRNAs miRNAs. DNA methylation histone modifications and noncoding RNA see FIGURE 1.
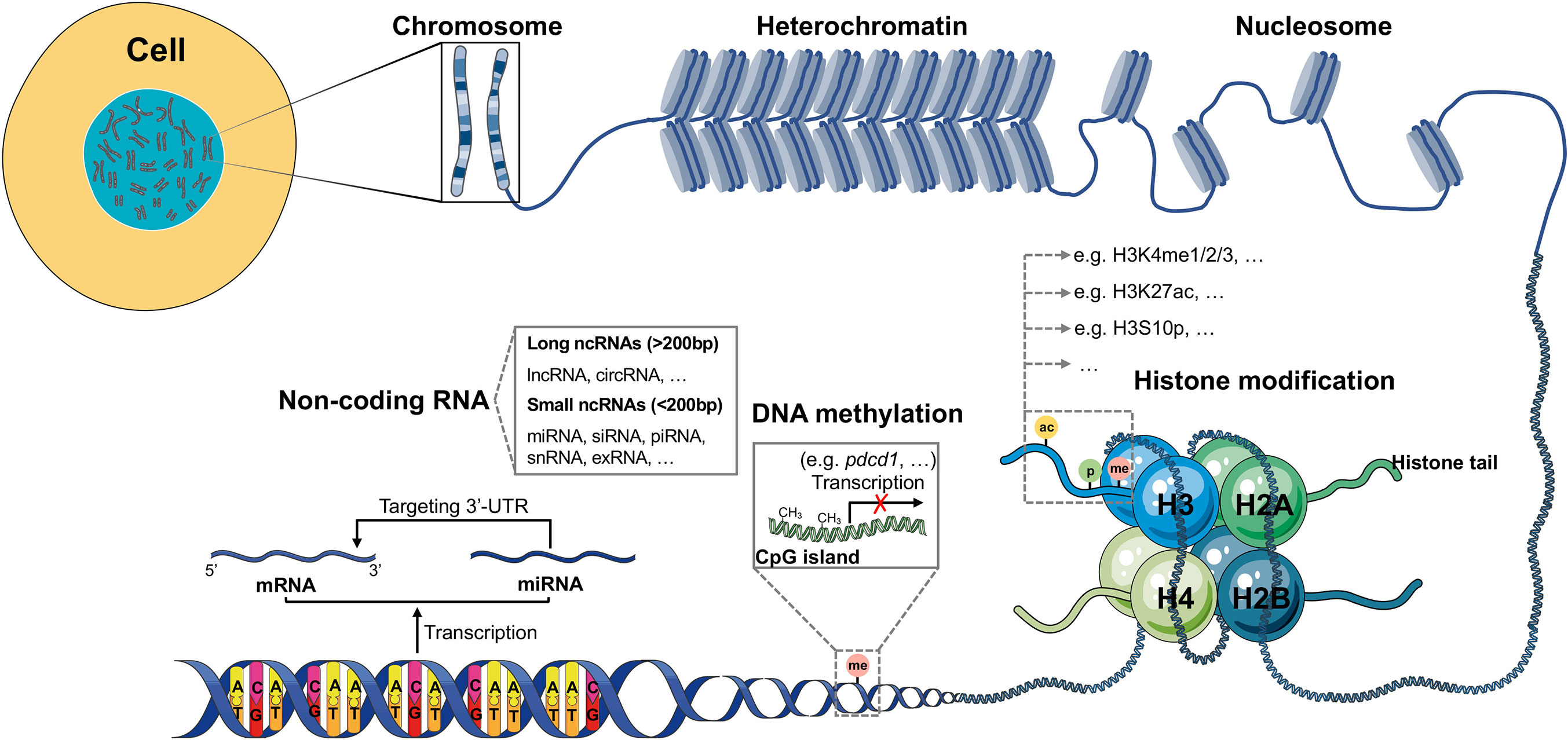 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
That is if you include as methylation the opposite demethylation and acetylation deacetylation. Epigenetics are heritable changes in gene expression that occur with no alteration in DNA sequence. DNA methylation histone modifications and noncoding RNA see FIGURE 1. These are functionally relevant changes and modifications of genome that excludes modifications of nucleotide sequences. Epigenetic modifications comprise three main mechanisms DNA methylation chromatin structure modifications and noncoding RNA ncRNA.
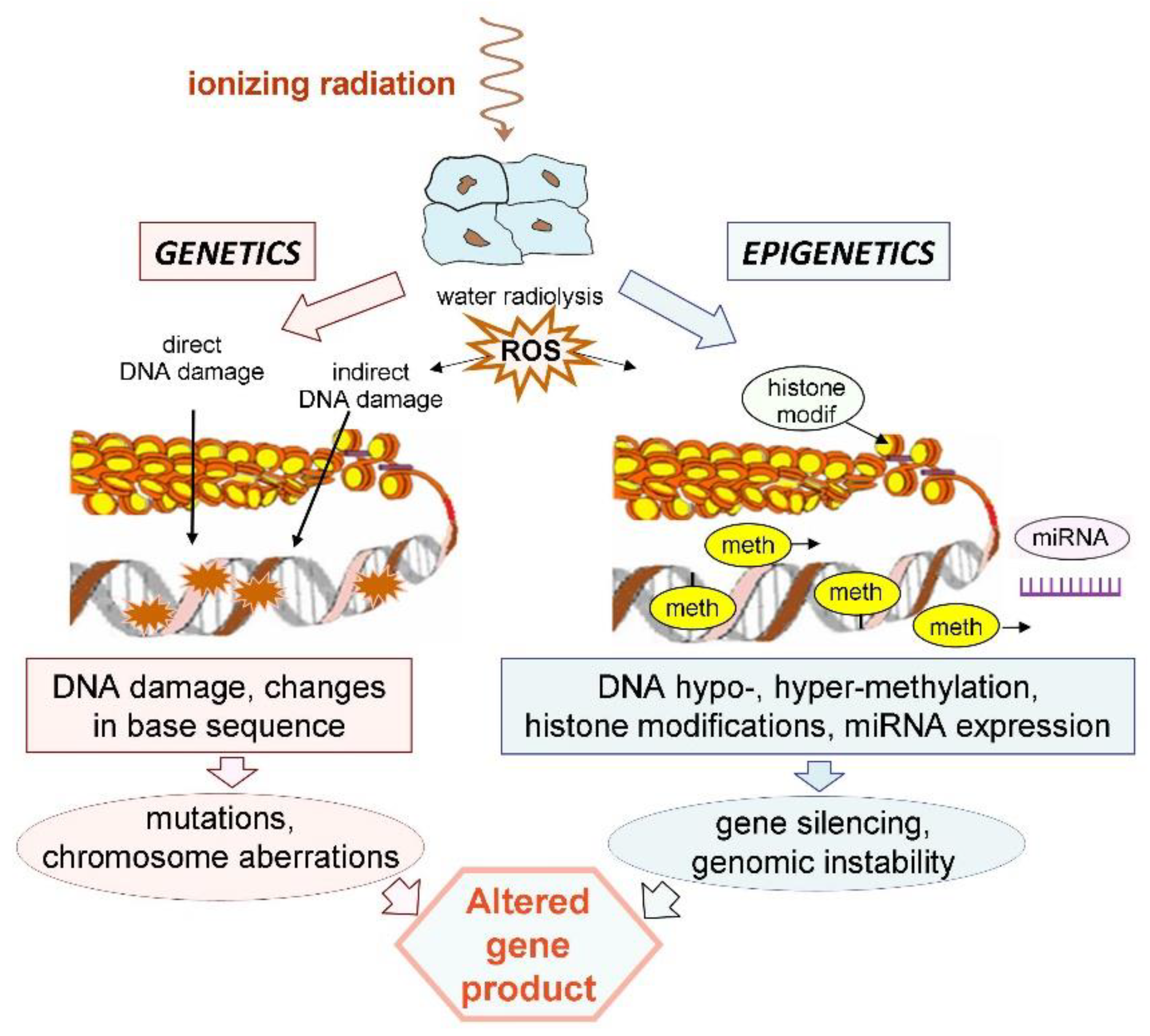 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
There are dynamic event that modulate the gene expression. Epigenetics refers to mechanisms of gene expression regulation that do not involve changes to the underlying DNA sequence. A number of epigenetic processes have been identified to play a role in IPF including the three major epigenetic mechanisms. There are three major processes of epigenetic modification. All these epigenetic mechanisms have important roles in the development of germ cells from primordial germ cell PGC differentiation and migration through meiotic process and maturation of functional gametes.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what are the major mechanisms of epigenetic genome modification by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





