Your Reversible covalent modification images are ready. Reversible covalent modification are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Reversible covalent modification files here. Get all free images.
If you’re looking for reversible covalent modification pictures information linked to the reversible covalent modification keyword, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always gives you hints for seeing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Reversible Covalent Modification. Reversible inhibitors are extremely important in regulating enzyme activity. Control proteins are protein subunits that associate with certain enzymes to activate or inhibit their activity. Become a member and unlock all Study Answers. In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell.
 How Do You Solve A Stoichiometry Problem Example Stoichiometry Chemistry Chemical Equation Teaching Chemistry From pinterest.com
How Do You Solve A Stoichiometry Problem Example Stoichiometry Chemistry Chemical Equation Teaching Chemistry From pinterest.com
Ø Here catalytic activity is modulated by reversible covalent modification of enzyme Ø More than 500 different molecules are known to modify enzymes by this method Ø Most common modifying groups include phosphoryl acetyl adenylyl uridylyl methyl amide carboxyl prenyl hydroxyl sulfate and adenosine diphosphate ribosyl groups. Control proteins are protein subunits that associate with certain enzymes to activate or inhibit their activity. Most often the reversible covalent modification of an enzyme involves the modification of a single or only a few amino acid side chains usually by a different enzyme. The discovery of protein ligands capable of forming a reversible covalent bond with amino acid residues on a protein target of interest may represent a general. So today were going to learn about covalent modifications to enzymes but first lets review the idea that enzymes make reactions go faster and looking at a reaction coordinate diagram youd notice that enzymes do this by lowering the reactions activation energy also before we talk about covalently modified enzymes I want to remind you that not all enzymes are proteins and often when we think of enzymes. Reversible covalent modifications require expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell.
The latter compound alone in fact causes a very small amount of alkylation.
1 Reversible covalent modifications. 1 Reversible covalent modifications. Reversible inhibitors are extremely important in regulating enzyme activity. Proteolytic Cleavage and Reversible Covalent Modification. TRP channel activation by reversible covalent modification Andrew Hinman Huai-hu Chuang Diana M. The Taunton group further shows the residence time of a reversible covalent drug can be systematically tuned via structural modification of the α-cyanoacrylamide warhead 10.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Coli isocitrate dehydrogenase involves the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a serine residue by the AceK kinase-phosphatase 15 16. The discovery of protein ligands capable of forming a reversible covalent bond with amino acid residues on a protein target of interest may represent a general. REVERSIBLE COVALENT MODIFICATION OF DNA 309 priate conditions a mixture of para-Il and para-bromomethylbenzoate gives greater binding than either separately R. This involves the addition and removal of some groups. 1 Reversible covalent modifications.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Proteolytic Cleavage and Reversible Covalent Modification. They can turn enzymes on or off acting as activators or inhibitors respectively. In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell. In most instances there are different enzymes responsible for the forward and reverse reactions. This involves the addition and removal of some groups.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. The latter compound alone in fact causes a very small amount of alkylation. Try it risk-free for 30 days. This involves the addition and removal of some groups. Reversible Covalent Modifications.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Try it risk-free for 30 days. Reversible covalent modification is when some enzymes are activated or deactivated by phosphorylation or the addition of some other modifier. Proteolytic Cleavage and Reversible Covalent Modification. Ø Here catalytic activity is modulated by reversible covalent modification of enzyme Ø More than 500 different molecules are known to modify enzymes by this method Ø Most common modifying groups include phosphoryl acetyl adenylyl uridylyl methyl amide carboxyl prenyl hydroxyl sulfate and adenosine diphosphate ribosyl groups. The mechanism of AITC action is in many ways similar to a variety of endogenous cellular signaling processes such as phosphorylation or disulfide bonding in which small reversible covalent modifications produce conformational changes in protein structure that.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
GoConqr is a personal learning environment that allows students teachers to create discover and share learning resources. TRP channel activation by reversible covalent modification Andrew Hinman Huai-hu Chuang Diana M. Proteolytic Cleavage and Reversible Covalent Modification - YouTube. Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. 1 Reversible covalent modifications.
 Source: tuitiontube.com
Source: tuitiontube.com
1 Reversible covalent modifications. Control proteins are protein subunits that associate with certain enzymes to activate or inhibit their activity. So today were going to learn about covalent modifications to enzymes but first lets review the idea that enzymes make reactions go faster and looking at a reaction coordinate diagram youd notice that enzymes do this by lowering the reactions activation energy also before we talk about covalently modified enzymes I want to remind you that not all enzymes are proteins and often when we think of enzymes. Transform your learning and achieve your goals with GoConqr. Specifically a series of BTK kinase inhibitors displaying end-capped α-cyanoacrylamide warheads were synthesized and found to display biochemical residence times ranging from minutes to seven days Figure 2 c.
 Source: en.wikibooks.org
Source: en.wikibooks.org
In most instances there are different enzymes responsible for the forward and reverse reactions. Become a member and unlock all Study Answers. The latter compound alone in fact causes a very small amount of alkylation. In most instances there are different enzymes responsible for the forward and reverse reactions. Reversible modifications typically associated with the regulation of signalling and metabolic processes and select critical targets can be modified by multiple types of modifications at multiple types of amino acids with multiple number of.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The modification of the protein can be reversible or irreversible. Try it risk-free for 30 days. Control proteins are protein subunits that associate with certain enzymes to activate or inhibit their activity. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. REVERSIBLE COVALENT MODIFICATION OF DNA 309 priate conditions a mixture of para-Il and para-bromomethylbenzoate gives greater binding than either separately R.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This is an example of reversible covalent modification. Bautista and David Julius Departments of Physiology and Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology University of California San Francisco CA 94158 Contributed by David Julius October 30 2006 sent for review October 4 2006. In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell. Try it risk-free for 30 days. Reversible Covalent Modifications.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Coli isocitrate dehydrogenase involves the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a serine residue by the AceK kinase-phosphatase 15 16. Control proteins are protein subunits that associate with certain enzymes to activate or inhibit their activity. Reversible covalent modifications require expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell Reversible covalent modifications that are known to alter enzyme activity include. For example the regulation of the specific activity of E. Proteolytic Cleavage and Reversible Covalent Modification.
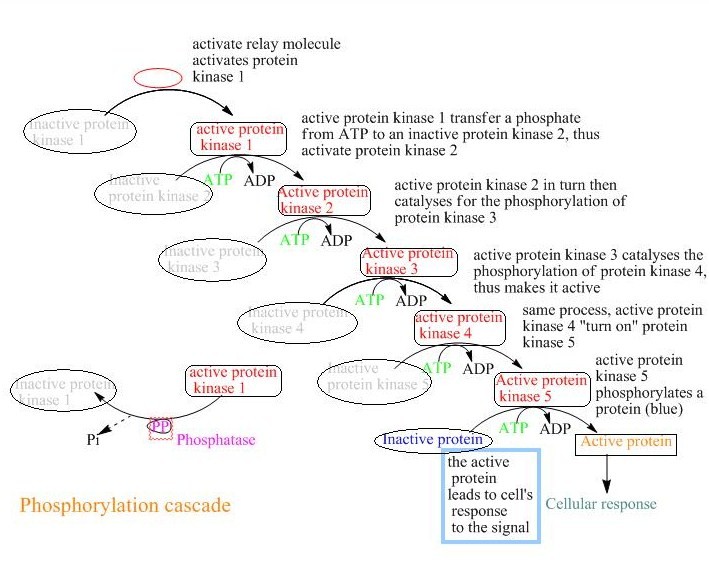 Source: en.wikibooks.org
Source: en.wikibooks.org
REVERSIBLE COVALENT MODIFICATION OF DNA 309 priate conditions a mixture of para-Il and para-bromomethylbenzoate gives greater binding than either separately R. Reversible covalent modifications require an expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages. The discovery of protein ligands capable of forming a reversible covalent bond with amino acid residues on a protein target of interest may represent a general. GoConqr is a personal learning environment that allows students teachers to create discover and share learning resources. Become a member and unlock all Study Answers.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
TRP channel activation by reversible covalent modification Andrew Hinman Huai-hu Chuang Diana M. Proteolytic Cleavage and Reversible Covalent Modification - YouTube. REVERSIBLE COVALENT MODIFICATION OF DNA 309 priate conditions a mixture of para-Il and para-bromomethylbenzoate gives greater binding than either separately R. Coli isocitrate dehydrogenase involves the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a serine residue by the AceK kinase-phosphatase 15 16. Covalent Modification Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The mechanism of AITC action is in many ways similar to a variety of endogenous cellular signaling processes such as phosphorylation or disulfide bonding in which small reversible covalent modifications produce conformational changes in protein structure that. Try it risk-free for 30 days. Coli isocitrate dehydrogenase involves the phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a serine residue by the AceK kinase-phosphatase 15 16. 1 Reversible covalent modifications. So today were going to learn about covalent modifications to enzymes but first lets review the idea that enzymes make reactions go faster and looking at a reaction coordinate diagram youd notice that enzymes do this by lowering the reactions activation energy also before we talk about covalently modified enzymes I want to remind you that not all enzymes are proteins and often when we think of enzymes.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The discovery of protein ligands capable of forming a reversible covalent bond with amino acid residues on a protein target of interest may represent a general. Reversible modifications typically associated with the regulation of signalling and metabolic processes and select critical targets can be modified by multiple types of modifications at multiple types of amino acids with multiple number of. Try it risk-free for 30 days. Transform your learning and achieve your goals with GoConqr. Reversible covalent modifications require expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Reversible Covalent Modifications. 1 Reversible covalent modifications. Become a member and unlock all Study Answers. REVERSIBLE COVALENT MODIFICATION OF DNA 309 priate conditions a mixture of para-Il and para-bromomethylbenzoate gives greater binding than either separately R. The Taunton group further shows the residence time of a reversible covalent drug can be systematically tuned via structural modification of the α-cyanoacrylamide warhead 10.
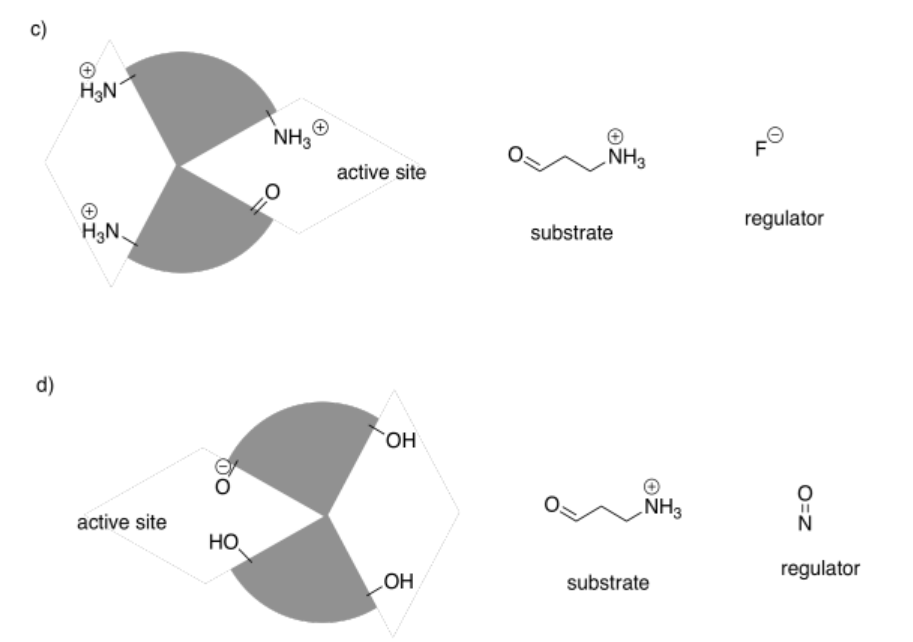 Source: chem.libretexts.org
Source: chem.libretexts.org
REVERSIBLE COVALENT MODIFICATION OF DNA 309 priate conditions a mixture of para-Il and para-bromomethylbenzoate gives greater binding than either separately R. Proteolytic Cleavage and Reversible Covalent Modification - YouTube. Become a member and unlock all Study Answers. The latter compound alone in fact causes a very small amount of alkylation. Specifically a series of BTK kinase inhibitors displaying end-capped α-cyanoacrylamide warheads were synthesized and found to display biochemical residence times ranging from minutes to seven days Figure 2 c.
 Source: tuitiontube.com
Source: tuitiontube.com
Reversible covalent modifications require expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell Reversible covalent modifications that are known to alter enzyme activity include. Reversible covalent modifications require an expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages. The mechanism of AITC action is in many ways similar to a variety of endogenous cellular signaling processes such as phosphorylation or disulfide bonding in which small reversible covalent modifications produce conformational changes in protein structure that. Reversible covalent modifications require expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell. The modification of the protein can be reversible or irreversible.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Reversible inhibitors are extremely important in regulating enzyme activity. This is an example of reversible covalent modification. Reversible covalent modification is when some enzymes are activated or deactivated by phosphorylation or the addition of some other modifier. Reversible covalent changes are known to change the activity of the enzyme such as. Reversible covalent modifications require expenditure of energy and are often used in signaling from extracellular messages In contrast noncovalent interactions are reversible with no metabolic energy expended and sense conditions within a cell Reversible covalent modifications that are known to alter enzyme activity include.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title reversible covalent modification by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






