Your Covalent modification definition images are available in this site. Covalent modification definition are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Covalent modification definition files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for covalent modification definition images information linked to the covalent modification definition keyword, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always gives you hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
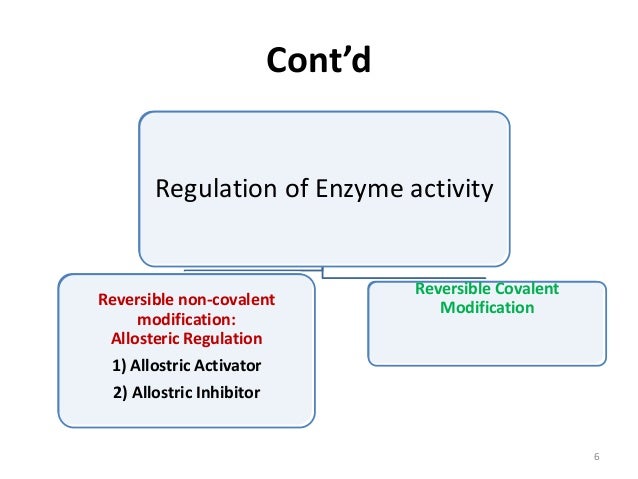
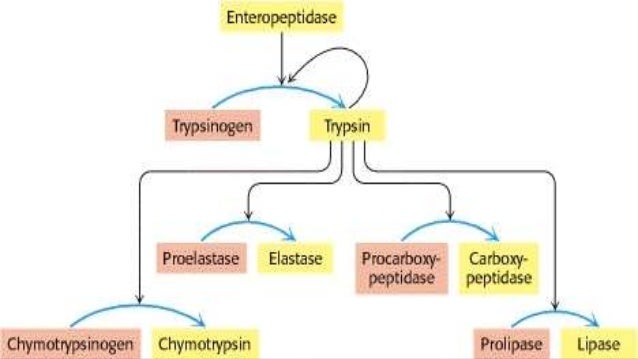
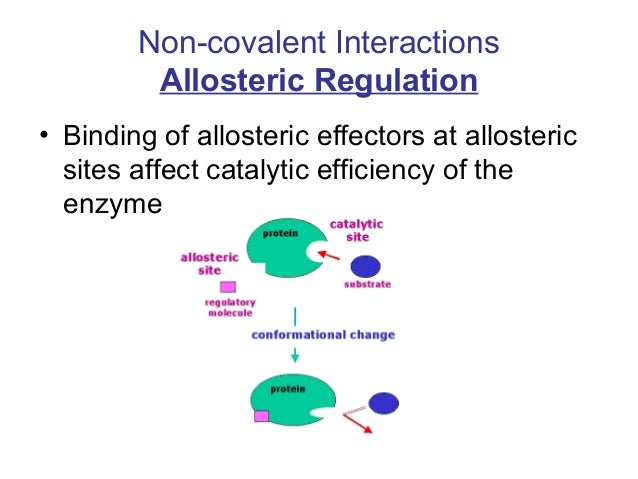
Covalent Modification Definition. Covalent carbon nanotube CNT derivatization. Systematic variation in a characteristic for example frequency amplitude of a sustained oscillation to code additional information. Covalent modification alteration in the structure of a macromolecule by enzymatic means resulting in a change in the properties of that macromolecule. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage.
 Regulatory And Allosteric Enzymes And Allostrerism From slideshare.net
Regulatory And Allosteric Enzymes And Allostrerism From slideshare.net
Systematic variation in a characteristic for example frequency amplitude of a sustained oscillation to code additional information. Functionality that cannot be introduced into COFs directly via de novo syntheses can be accessed through post-synthetic modification PSM strategies. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. The covalent enzyme modification is mainly in two types. Watch the next lesson. CNT covalent modification Definition Covalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes CNTs is the attachment of chemical moieties to the CNT tubular structure via the formation of covalent bonds which share at least one pair of electrons between the CNT and the introduced chemical moiety.
CNT covalent modification Definition Covalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes CNTs is the attachment of chemical moieties to the CNT tubular structure via the formation of covalent bonds which share at least one pair of electrons between the CNT and the introduced chemical moiety.
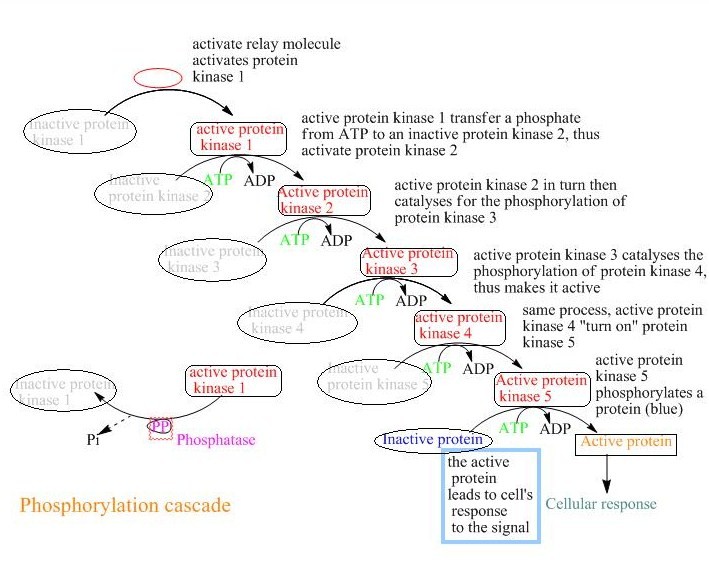
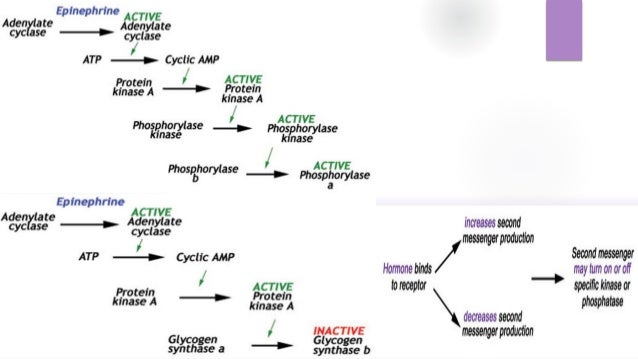
Videos you watch may be added to the TVs watch history and influence TV recommendations. Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. Examples of Covalent Modification. May be either stimulatory or inhibitory. A passing or transition from one key or tonality to another. The most remarkable covalent modification is phosphorylation.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Systematic variation in a characteristic for example frequency amplitude of a sustained oscillation to code additional information. CNT covalent modification Definition Covalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes CNTs is the attachment of chemical moieties to the CNT tubular structure via the formation of covalent bonds which share at least one pair of electrons between the CNT and the introduced chemical moiety. The phosphorylation of particular serine threonine or tyrosine. 1 Allosteric is non covalent. The covalent enzyme modification is mainly in two types.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
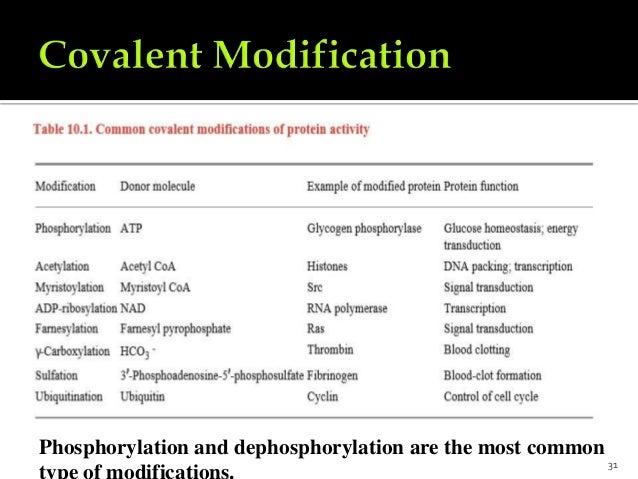
These groups are joined to or eliminated from the protein by other enzymes. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary. The most remarkable covalent modification is phosphorylation. Stimulator is often the substrate. Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Watch the next lesson. Covalent enzyme modification is a process of regulating the activity of an enzyme. Examples of Covalent Modification. The most remarkable covalent modification is phosphorylation. A covalent bond may also be termed a molecular bond.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Systematic variation in a characteristic for example frequency amplitude of a sustained oscillation to code additional information. In metabolic control modulation of enzyme activity by attaching or releasing tiny groups plays a very significant role. Videos you watch may be added to the TVs watch history and influence TV recommendations. Serine Threonine and Tyrosine are common amino acids that participate in covalent modifications and are used to control enzymes catalytic activities. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. These groups are joined to or eliminated from the protein by other enzymes. Covalent organic frameworks COFs are organic porous materials with many potential applications which very often depend on the presence of chemical functionality at the organic building blocks. The phosphorylation of particular serine threonine or tyrosine. 1 Allosteric is non covalent.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Or cases where the natural ligand has extremely high affinity or is present in high concentrations eg. Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. They are- Reversible covalent modification. The covalent enzyme modification is mainly in two types. Sulfur is amenable to covalent modification due to the nucleophilicity of sulfur and as such there are examples of ligands that modify cysteine in.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
A passing or transition from one key or tonality to another. Amino acids capable of covalent modification are typically those which have a heteroatom such as O S or N in the side chain such as threonine cysteine histidine serine tyrosine and lysine. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary. Sulfur is amenable to covalent modification due to the nucleophilicity of sulfur and as such there are examples of ligands that modify cysteine in. Covalent carbon nanotube CNT derivatization.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
May be either stimulatory or inhibitory. Systematic variation in a characteristic for example frequency amplitude of a sustained oscillation to code additional information. The phosphorylation of particular serine threonine or tyrosine. The most remarkable covalent modification is phosphorylation. Examples of Covalent Modification.
 Source: tuitiontube.com
Source: tuitiontube.com
Amino acids capable of covalent modification are typically those which have a heteroatom such as O S or N in the side chain such as threonine cysteine histidine serine tyrosine and lysine. Covalent organic frameworks COFs are organic porous materials with many potential applications which very often depend on the presence of chemical functionality at the organic building blocks. CNT covalent modification Definition Covalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes CNTs is the attachment of chemical moieties to the CNT tubular structure via the formation of covalent bonds which share at least one pair of electrons between the CNT and the introduced chemical moiety. The functional and morphologic fluctuation of cells in response to changing environmental conditions. May be either stimulatory or inhibitory.
 Source: en.wikibooks.org
Source: en.wikibooks.org
Frequently this type of modification is physiologically relevant. These groups are joined to or eliminated from the protein by other enzymes. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Amino acids capable of covalent modification are typically those which have a heteroatom such as O S or N in the side chain such as threonine cysteine histidine serine tyrosine and lysine.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Stimulator is often the substrate. In metabolic control modulation of enzyme activity by attaching or releasing tiny groups plays a very significant role. The functional and morphologic fluctuation of cells in response to changing environmental conditions. Covalent Enzyme modification. A covalent bond in chemistry is a chemical link between two atoms or ions in which the electron pairs are shared between them.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
They are- Reversible covalent modification. The covalent enzyme modification is mainly in two types. A covalent bond may also be termed a molecular bond. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
May be either stimulatory or inhibitory. To avoid this cancel. The covalent enzyme modification is mainly in two types. Covalent Enzyme modification. Covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms with identical or.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
A covalent bond in chemistry is a chemical link between two atoms or ions in which the electron pairs are shared between them. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. Frequently this type of modification is physiologically relevant. In metabolic control modulation of enzyme activity by attaching or releasing tiny groups plays a very significant role. They are- Reversible covalent modification.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Examples of Covalent Modification. May be either stimulatory or inhibitory. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage. Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Sulfur is amenable to covalent modification due to the nucleophilicity of sulfur and as such there are examples of ligands that modify cysteine in.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Videos you watch may be added to the TVs watch history and influence TV recommendations. Serine Threonine and Tyrosine are common amino acids that participate in covalent modifications and are used to control enzymes catalytic activities. Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Stimulator is often the substrate. Covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms with identical or.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
A passing or transition from one key or tonality to another. Serine Threonine and Tyrosine are common amino acids that participate in covalent modifications and are used to control enzymes catalytic activities. 1 Allosteric is non covalent. CNT covalent modification Definition Covalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes CNTs is the attachment of chemical moieties to the CNT tubular structure via the formation of covalent bonds which share at least one pair of electrons between the CNT and the introduced chemical moiety. Another way of regulating an enzyme is by altering the amino acid sequence itself by proteolytic cleavage.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
CNT covalent modification Definition Covalent functionalization of carbon nanotubes CNTs is the attachment of chemical moieties to the CNT tubular structure via the formation of covalent bonds which share at least one pair of electrons between the CNT and the introduced chemical moiety. Amino acids capable of covalent modification are typically those which have a heteroatom such as O S or N in the side chain such as threonine cysteine histidine serine tyrosine and lysine. Covalent bonds form between two nonmetal atoms with identical or. Enzymes can be regulated by transfer of a molecule or atom from a donor to an amino acid side chain that serves as the acceptor of the transferred molecule. Systematic variation in a characteristic for example frequency amplitude of a sustained oscillation to code additional information.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title covalent modification definition by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





